DevOps Best Practices: From Development to Production
Published on October 22, 2025 by durga
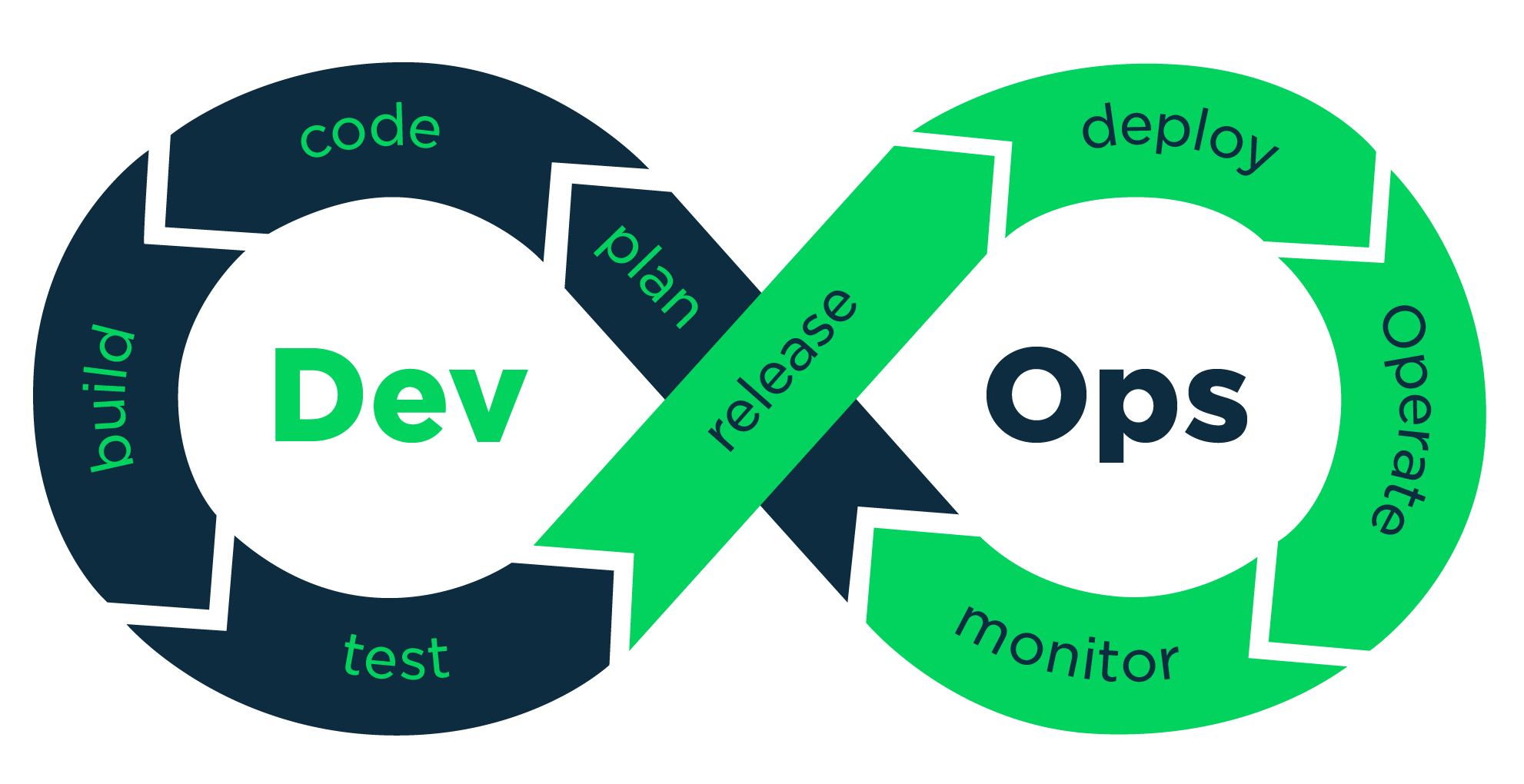
DevOps has transformed how we build, deploy, and maintain software. This comprehensive guide covers essential practices that bridge the gap between development and operations teams.
Core DevOps Principles
1. Culture and Collaboration
DevOps is fundamentally about breaking down silos between development, operations, and other stakeholders.
2. Automation
Automate repetitive tasks to reduce errors, increase efficiency, and enable faster delivery.
3. Continuous Integration and Deployment
Integrate code changes frequently and deploy to production safely and reliably.
4. Monitoring and Feedback
Continuously monitor applications and infrastructure to gather feedback for improvement.
CI/CD Pipeline Implementation
Continuous Integration (CI)
CI involves automatically building, testing, and validating code changes:
- Source Control: Use Git with branching strategies like GitFlow or GitHub Flow
- Automated Testing: Unit tests, integration tests, and code quality checks
- Build Automation: Consistent and repeatable build processes
- Artifact Management: Store and version build artifacts
Continuous Deployment (CD)
CD automates the deployment of validated changes to production:
- Deployment Automation: Scripted deployment processes
- Environment Management: Consistent environments across the pipeline
- Rollback Strategies: Quick recovery from failed deployments
- Blue-Green Deployments: Zero-downtime deployments
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Benefits of IaC:
- Version-controlled infrastructure
- Consistent and repeatable deployments
- Reduced configuration drift
- Faster environment provisioning
Popular IaC Tools:
- Terraform: Multi-cloud infrastructure provisioning
- AWS CloudFormation: AWS-native infrastructure automation
- Azure Resource Manager: Azure infrastructure templates
- Ansible: Configuration management and automation
- Pulumi: Modern infrastructure as code with programming languages
Containerization and Orchestration
Docker Benefits:
- Consistent runtime environments
- Improved resource utilization
- Simplified deployment processes
- Enhanced scalability
Kubernetes for Orchestration:
- Automated container deployment and scaling
- Service discovery and load balancing
- Rolling updates and rollbacks
- Resource management and optimization
Monitoring and Observability
Three Pillars of Observability:
1. Metrics
- Application performance metrics
- Infrastructure metrics
- Business metrics
- Custom application metrics
2. Logs
- Structured logging
- Centralized log aggregation
- Log analysis and correlation
- Security and audit logs
3. Traces
- Distributed tracing
- Request flow visualization
- Performance bottleneck identification
- Service dependency mapping
Monitoring Tools:
- Prometheus + Grafana: Metrics collection and visualization
- ELK Stack: Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana for log management
- Jaeger/Zipkin: Distributed tracing
- DataDog: Comprehensive monitoring platform
- New Relic: Application performance monitoring
Security in DevOps (DevSecOps)
Shift-Left Security:
- Security checks in CI/CD pipelines
- Static application security testing (SAST)
- Dynamic application security testing (DAST)
- Dependency vulnerability scanning
- Container image security scanning
Security Tools Integration:
- SonarQube: Code quality and security analysis
- OWASP ZAP: Web application security testing
- Snyk: Dependency vulnerability management
- Aqua Security: Container and cloud security
Testing Strategies
Test Pyramid:
- Unit Tests: Fast, isolated tests for individual components
- Integration Tests: Test interactions between components
- End-to-End Tests: Test complete user workflows
Testing in Production:
- Canary deployments
- Feature flags
- A/B testing
- Chaos engineering
Performance and Scalability
Application Performance:
- Performance testing in CI/CD
- Load testing and stress testing
- Performance benchmarking
- Resource optimization
Auto-scaling Strategies:
- Horizontal pod autoscaling (HPA)
- Vertical pod autoscaling (VPA)
- Cluster autoscaling
- Predictive scaling
DevOps Metrics and KPIs
DORA Metrics:
- Deployment Frequency: How often deployments occur
- Lead Time for Changes: Time from code commit to production
- Change Failure Rate: Percentage of deployments causing failures
- Time to Recovery: Time to recover from failures
Additional Metrics:
- Mean Time to Detection (MTTD)
- Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR)
- Code coverage percentage
- Infrastructure cost optimization
Common Challenges and Solutions
Cultural Resistance:
- Start with willing teams and show success
- Provide training and support
- Celebrate wins and learn from failures
Tool Proliferation:
- Standardize on core toolchain
- Evaluate tools based on integration capabilities
- Avoid vendor lock-in where possible
Legacy Systems:
- Gradual modernization approach
- Strangler pattern for legacy migration
- API-first approach for integration
Successful DevOps implementation requires commitment to cultural change, process improvement, and continuous learning. Start small, measure progress, and iterate based on feedback to build a robust DevOps practice.
